Calorimetry - Wikipedia calorimetru. Calorimetry has a special benefit for thermodynamics. It tells about the heat absorbed or emitted in the isothermal segment of a Carnot cycle. A Carnot cycle is a special kind of cyclic process affecting a body composed of material suitable for use in a heat engine calorimetru. Such a material is of the kind considered in calorimetry, as noted above, that .. Calorimeter | Definition, Uses, Diagram, & Facts | Britannica. Calorimeter, device for measuring the heat developed during a mechanical, electrical, or chemical reaction and for calculating the heat capacity of materials. The bomb calorimeter has an enclosure in which the reaction happens, surrounded by a liquid that absorbs the reactions heat and increases in temperature.. Calorimeter - Wikipedia. The worlds first ice-calorimeter, used in the winter of 1782-83, by Antoine Lavoisier and Pierre-Simon Laplace, to determine the heat evolved in various chemical changes; calculations which were based on Joseph Blacks prior discovery of latent heat.These experiments mark the foundation of thermochemistry. A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the . calorimetru. Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts
Calorimetru
rahimde polip
Calorimetry - Wikipedia calorimetru. Calorimetry has a special benefit for thermodynamics. It tells about the heat absorbed or emitted in the isothermal segment of a Carnot cycle. A Carnot cycle is a special kind of cyclic process affecting a body composed of material suitable for use in a heat engine calorimetru. Such a material is of the kind considered in calorimetry, as noted above, that .. Calorimeter | Definition, Uses, Diagram, & Facts | Britannica. Calorimeter, device for measuring the heat developed during a mechanical, electrical, or chemical reaction and for calculating the heat capacity of materials. The bomb calorimeter has an enclosure in which the reaction happens, surrounded by a liquid that absorbs the reactions heat and increases in temperature.. Calorimeter - Wikipedia. The worlds first ice-calorimeter, used in the winter of 1782-83, by Antoine Lavoisier and Pierre-Simon Laplace, to determine the heat evolved in various chemical changes; calculations which were based on Joseph Blacks prior discovery of latent heat.These experiments mark the foundation of thermochemistry. A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the . calorimetru. Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts
codigo postal de barranca
. Calorimetry. Because calorimetry is used to measure the heat of a reaction, it is a crucial part of thermodynamics. In order to measure the heat of a reaction, the reaction must be isolated so that no heat is lost to the environment. This is achieved by use of a calorimeter, which insulates the reaction to better contain heat.. 5.2 Calorimetry - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax. One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as calorimetry. Calorimetry is used to measure amounts of heat transferred to or from a substance. To do so, the heat is exchanged with a calibrated object (calorimeter). The temperature change measured by the calorimeter is used to derive .. Understanding Calorimetry to Measure Heat Transfer - ThoughtCo calorimetru. Calorimetry is a method of measuring the heat transfer within a chemical reaction or other physical processes, such as a change between different states of matter. The term "calorimetry" comes from the Latin calor ("heat") and Greek metron ("measure"), so it means "measuring heat." Devices used to perform calorimetry measurements are called . calorimetru. Calorimeter Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster. calorimeter: [noun] an apparatus for measuring quantities of absorbed or emitted heat or for determining specific heats.. 5.6: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts. Heat Transfer Between Hot and Cold Objects in an Ideal Calorimeter. When a hot object (T H) is placed in thermal contact with a cold object (T C) energy is transferred between the two, but the rate of heat transfer from the hot to the cold is greater, so it cools down while the cold object heats up, until they reach the same temperature (T F).Once they are at the same temperature the system is .. 12.3: Heat Capacity, Enthalpy, and Calorimetry. Calorimetry is the set of techniques used to measure enthalpy changes during chemical processes. It uses devices called calorimeters, which measure the change in temperature when a chemical reaction is carried out. The magnitude of the temperature change depends on the amount of heat released or absorbed and on the heat capacity of the system.. 5.3: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts. Figure 5.3.4: In a simple calorimetry process, (a) heat, q, is transferred from the hot metal, M, to the cool water, W, until (b) both are at the same temperature. Two diagrams are shown and labeled a and b. Each diagram is composed of a rectangular container with a thermometer inserted inside from the top right corner.. Calorimetry | CHEM101 ONLINE: General Chemistry - Lumen Learning calorimetru. Calorimetry calorimetru. Calorimetry is the measurement of the transfer of heat into or out of a system during a chemical reaction or physical process.A calorimeter is an insulated container that is used to measure heat changes.The majority of reactions that can be analyzed in a calorimetry experiment are either liquids or aqueous solutions. A frequently used and inexpensive calorimeter is a set of nested .. Calorimeters and Calorimetry - The Physics Classroom Tutorial calorimetru. Calorimetry is the science associated with determining the changes in energy of a system by measuring the heat exchanged with the surroundings. Now that sounds very textbooky; but in this last part of Lesson 2, we are going to try to make some meaning of this definition of calorimetry.In physics class (and for some, in chemistry class), calorimetry labs are frequently performed in order to . calorimetru. 5.5: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts. Calorimetry is the set of techniques used to measure enthalpy changes during chemical processes. It uses devices called calorimeters, which measure the change in temperature when a chemical reaction is carried out. The magnitude of the temperature change depends on the amount of heat released or absorbed and on the heat capacity of the system.. 10.2 Calorimetry - Chemistry Fundamentals - University of Central .. Calorimetry is used to measure the amount of thermal energy transferred in a chemical or physical process. This requires careful measurement of the temperature change that occurs during the process and the masses of the system and surroundings calorimetru. These measured quantities are then used to compute the amount of heat produced or consumed in the .. Calorimetry - Chemistry | Socratic calorimetru. Calorimetry is the measurement of heat flow. Heat energy flows from a substance that has a higher temperature to a substance that has a lower temperature. The heat will continue to flow until both substances reach the same temperature, known as the final temperature calorimetru. A device called a calorimeter is used to measure heat flow.. Calorimeter - Definition, Uses, Types, Application, Diagram - BYJUS
arina hashimoto uncensord
. Calorimetry is applied extensively in the fields of thermochemistry in calculating the enthalpy, stability, heat capacity etc. What Is a Calorimeter? A calorimeter is a device used for heat measurements necessary for calorimetry. It mainly consists of a metallic vessel made of materials which are good conductors of electricity such as copper . calorimetru. Calorimetry - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. Calorimetry, particularly differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), is an effective analytical tool to characterize melting, crystallization, and mesomorphic transitions and to determine the corresponding enthalpy and entropy changes. The glass transition and other effects that show changes in either heat capacity or latent heat are also accessible.. Calorimètre — Wikipédia
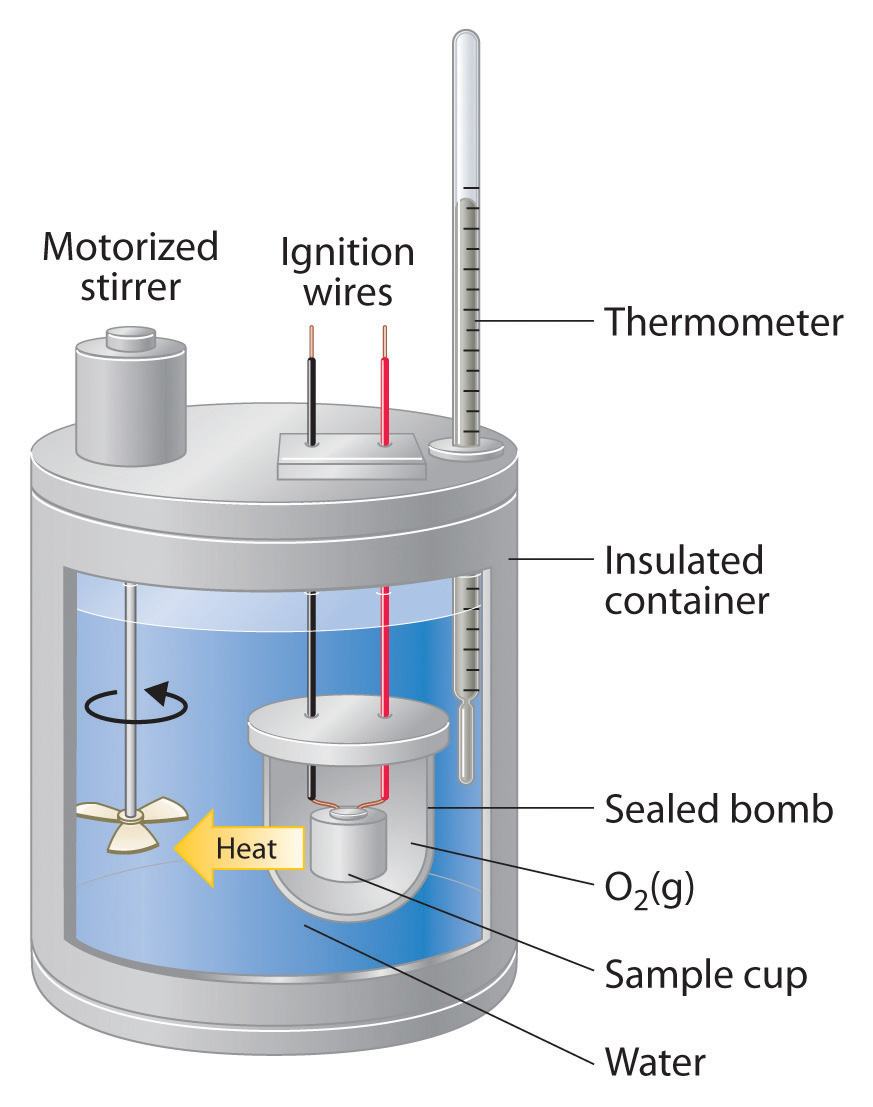
γιατι ποναει η ουροδοχος κυστη
. Contributors : Pascale Saba; Tulio Honorio; Xavier Brajer; Farid Benboudjema. Show more detail. calorimetru. Amira Guediche - PhD - Postdoctoral Researcher - LinkedIn. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Apr 2023 - Present 8 months. Livermore, Californie, États-Unis. Improving the performance of optical materials used in the National Ignition Facility (NIF .. Gabriel AYME - Principal Research Engineer - LinkedIn calorimetru. IH4 is a stable protein with a transition melting temperature of 75.8°C (measured by differential scanning calorimetry)
auto kuća bebić
. As proof of concept, we fused HIV p24 to IH4 and used the purified construct expressed in E. coli to show that IH4 was amenable to the preparation of autologous erythrocyte agglutination reagents: reconstituted blood . calorimetru. Principle of Calorimetry - Definition, Problems and more - BYJUS. Principle of Calorimetry. The Universe is made of matter and energy. The matter is made up of atoms and molecules, and energy invariably makes these atoms and molecules in motion - either by vibrating back and forth or bumping into each other. This motion of molecules and atoms creates a form of energy known as thermal energy or heat.. 5.3: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts. Exercise 5.3.2 5.3. 2. A 92.9-g piece of a silver/gray metal is heated to 178.0 °C, and then quickly transferred into 75.0 mL of water initially at 24.0 °C. After 5 minutes, both the metal and the water have reached the same temperature: 29.7 °C. Determine the specific heat and the identity of the metal.. 7.3: Heats of Reactions and Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts calorimetru. Calorimetry is the set of techniques used to measure enthalpy changes during chemical processes. It uses devices called calorimeters, which measure the change in temperature when a chemical reaction is carried out. The magnitude of the temperature change depends on the amount of heat released or absorbed and on the heat capacity of the system. calorimetru. 5: Experiment 5 - Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts. Calorimetry is the science of measuring heat flow. Heat is defined as thermal energy flowing from an object at a higher temperature to one at a lower temperature. For example, if you drop a coin into a cup with hot water, the temperature of the coin will go up until it is at the same temperature as the boiling water.. Calorimetry - Chemistry - UH Pressbooks. Calorimetry is used to measure the amount of thermal energy transferred in a chemical or physical process. This requires careful measurement of the temperature change that occurs during the process and the masses of the system and surroundings. These measured quantities are then used to compute the amount of heat produced or consumed in the .. Advances in Continuous Flow Calorimetry | Organic Process Research . calorimetru. Therefore, reaction calorimetry in continuous flow is a powerful technique that features higher yield, conversion, and selectivity and facilitates process automation. (18) Steady-state operation leads to the development of a temperature profile within the reactor, which can be analyzed for kinetic purposes.. 5.2: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts calorimetru. Figure 5.2.4 5.2. 4: In a simple calorimetry process, (a) heat, q, is transferred from the hot metal, M, to the cool water, W, until (b) both are at the same temperature. A 360.0-g piece of rebar (a steel rod used for reinforcing concrete) is dropped into 425 mL of water at 24.0 °C. calorimetru. 2.8: Heat of a Reaction and Coffee Cup Calorimeter-Home calorimetru. Calorimetry is used to measure the amount of thermal energy transferred in a chemical or physical process. This requires careful measurement of the temperature change that occurs during the process and the masses of the system and surroundings. These measured quantities are then used to compute the amount of heat produced or consumed in the .. Calorimeter Definition in Chemistry - ThoughtCo. Updated on August 19, 2019. A calorimeter is a device used to measure the heat flow of a chemical reaction or physical change. The process of measuring this heat is called calorimetry. A basic calorimeter consists of a metal container of water above a combustion chamber, in which a thermometer is used to measure the change in water temperature. calorimetru. 1.4 Heat Transfer, Specific Heat, and Calorimetry. Calculating the Final Temperature in Calorimetry Suppose you pour 0.250 kg of [latex]20.0-^circtext{C}[/latex] water (about a cup) into a .500-kg aluminum pan off the stove with a temperature of [latex]150^circtext{C}[/latex]. Assume no heat transfer takes place to anything else: The pan is placed on an insulated pad, and heat transfer to .. Heat capacity and calorimetry (practice) | Khan Academy. Heat capacity and calorimetry calorimetru. A 20. g iron rod is heated to a temperature T 1 and then dropped into 20. g of water at a lower temperature T 2 in a polystyrene cup calorimetru
application letter for zambia army recruitment
. Which of the following is true of the final temperature of the system when thermal equilibrium is reached? calorimetru. Constant-volume calorimetry (video) | Khan Academy calorimetru. Constant-volume calorimetry is used to measure the change in internal energy, ΔE, for a combustion reaction. In this technique, a sample is burned under constant volume in a device called a bomb calorimeter. The amount of heat released in the reaction can be calculated using the equation q = -CΔT, where C is the heat capacity of the .. Calorimetry Problems, Thermochemistry Practice, Specific Heat calorimetru. - YouTube calorimetru. This chemistry video tutorial explains how to solve calorimetry problems in thermochemistry. It shows you how to calculate the quantity of heat transferred . calorimetru. 6.2: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts calorimetru. 6.2: Calorimetry
colegio de abogados de tacna
. Calculate and interpret heat and related properties using typical calorimetry data. One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as calorimetry calorimetru. Calorimetry is used to measure amounts of heat transferred to or from a substance.. 8.2: Calorimetry (Problems) - Chemistry LibreTexts. PROBLEM 8.2. 1. A 500-mL bottle of water at room temperature and a 2-L bottle of water at the same temperature were placed in a refrigerator. After 30 minutes, the 500-mL bottle of water had cooled to the temperature of the refrigerator. An hour later, the 2-L of water had cooled to the same temperature. When asked which sample of water lost . calorimetru. A brief history of heat measurements by calorimetry with emphasis on .. The solution calorimetry method relies on rapid solution of both the components and the reacted products in the selected solvent. The solvent is usually a low melting metal such as tin, copper or aluminum. Usually this is a highly precise method and very useful for a wide variety of materials. It is important to ascertain that the solute does .. Heat Transfer, Specific Heat, and Calorimetry - Physics LibreTexts calorimetru. Heat Transfer and Temperature Change. A practical approximation for the relationship between heat transfer and temperature change is: Q = mcΔT, where Q is the symbol for heat transfer ("quantity of heat"), m is the mass of the substance, and ΔT is the change in temperature. The symbol c stands for the specific heat (also called .. 8.2: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts
murphy qanunu
. Calorimetry is used to measure the amount of thermal energy transferred in a chemical or physical process. This requires careful measurement of the temperature change that occurs during the process and the masses of the system and surroundings calorimetru. These measured quantities are then used to compute the amount of heat produced or consumed in the .. Heat capacity (video) | Thermodynamics | Khan Academy. Heat capacity is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a given amount of matter by 1°C. The heat capacity of 1 gram of a substance is called its specific heat capacity (or specific heat), while the heat capacity of 1 mole of a substance is called its molar heat capacity. The amount of heat gained or lost by a sample (q) can .. 17.7: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts. Calorimetry. Calorimetry is the measurement of the transfer of heat into or out of a system during a chemical reaction or physical process. A calorimeter is an insulated container that is used to measure heat changes. The majority of reactions that can be analyzed in a calorimetry experiment are either liquids or aqueous solutions. A frequently used and inexpensive calorimeter is a set of . calorimetru. AP Chem Unit 6.4 Heat Capacity & Calorimetry - Fiveable. Calorimetry. The absolute enthalpy of a system (H) cannot be measured directly, but changes in enthalpy (ΔH) can be measured using calorimetry. Calorimetry is the study of heat flow and heat exchange between a system and its surroundings and it can be used to calculate ΔH by measuring changes in temperature, which represent heat being lost or gained calorimetru. .. Constant-pressure calorimetry (video) | Khan Academy
აწმყოს ძალა
. A calorimeter is a tool that can be used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process calorimetru. Read More: Latent Heat of Water. Principle of Calorimetry. Calorimetry | General Chemistry - Lumen Learning. calorimetry: process of measuring the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process calorimetru. nutritional calorie (Calorie): unit used for quantifying energy provided by digestion of foods, defined as 1000 cal or 1 kcal. surroundings: all matter other than the system being studied. calorimetru. Heat Measurement - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. Calorimetry, particularly differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), is an effective analytical tool to characterize melting, crystallization, and mesomorphic transitions and to determine the corresponding enthalpy and entropy changes. The glass transition and other effects that show changes in either heat capacity or latent heat are also accessible. calorimetru. 7.5: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts. Calorimetry is the set of techniques used to measure enthalpy changes during chemical processes. It uses devices called calorimeters, which measure the change in temperature when a chemical reaction is carried out. The magnitude of the temperature change depends on the amount of heat released or absorbed and on the heat capacity of the system.. Calorimetry, Specific Heat, and Calculations - AP Chemistry. Plug in known values to the equation and solve. Our answer must contain three significant figures. To find the amount of heat needed to change the temperature of a given material by a certain amount, well need to use the equation for specific heat calorimetru. The specific heat capacity of a compound represents the amount of energy necessary to raise.. Calorimetry - UCalgary Chemistry Textbook. Calorimetry. Objectives: One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as calorimetry. Calorimetry is used to measure amounts of heat transferred to or from a substance. To do so, the heat is exchanged with a calibrated object (calorimeter).. 6.4: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts. Figure 6.4.4: In a simple calorimetry process, (a) heat, q, is transferred from the hot metal, M, to the cool water, W, until (b) both are at the same temperature calorimetru. A hot 360-g piece of rebar (a steel rod used for reinforcing concrete) is dropped into 425 mL of water at 24.0 °C.. 3.3: Calorimetry - Engineering LibreTexts calorimetru. Figure 3.3.4: In a simple calorimetry process, (a) heat, q, is transferred from the hot metal, M, to the cool water, W, until (b) both are at the same temperature
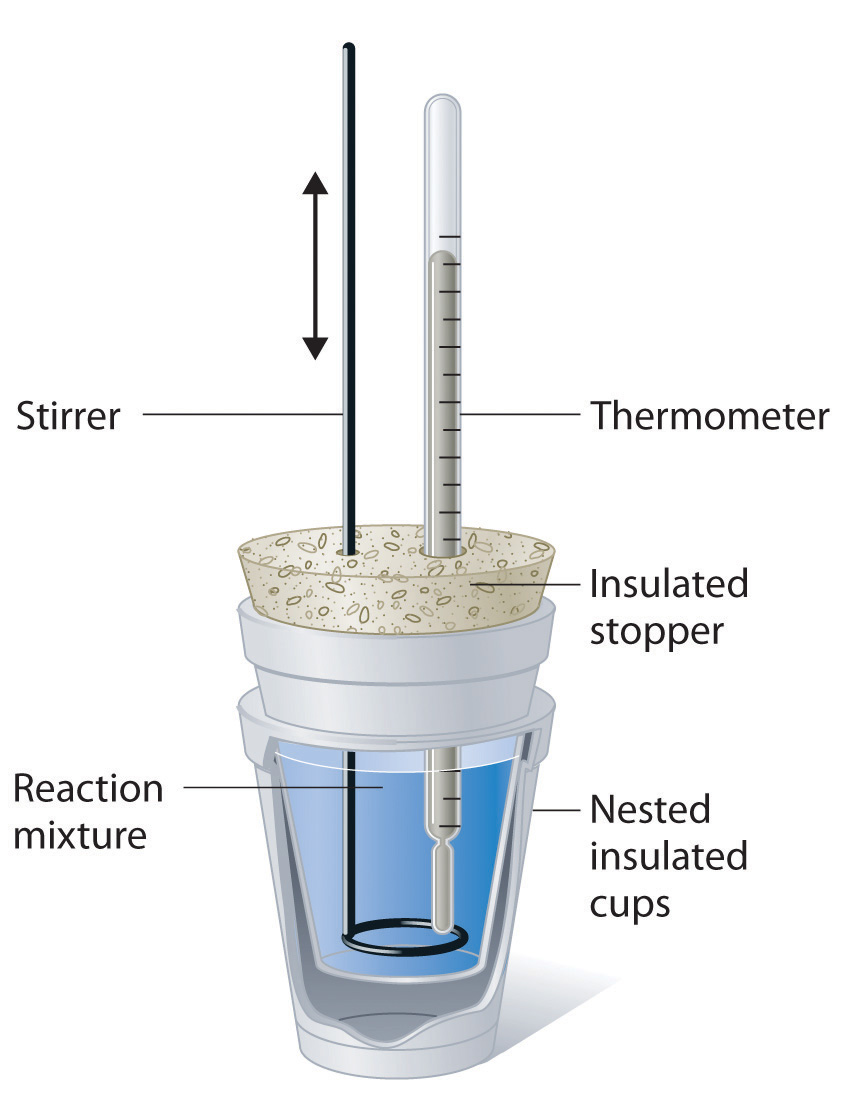
. Like the word "calorie," the term is derived from a Latin root meaning "heat." The foundations of calorimetry go back to the mid-nineteenth century, but the field owes much to scientists work that took .. 14.5: Calorimetry - Chemistry LibreTexts. Introduction. Calorimetry is used to measure quantities of heat, and can be used to determine the heat of a reaction through experiments. Usually a coffee-cup calorimeter is used since it is simpler than a bomb calorimeter, but to measure the heat evolved in a combustion reaction, constant volume or bomb calorimetry is ideal. A constant volume calorimeter is also more accurate than a coffee .. Calorimetry Techniques | SpringerLink calorimetru. Calorimetry is quite an old but complex technique that is capable of directly measuring the heat associated with any physical transformations or chemical reactions calorimetru. In the past few decades, the calorimetry techniques underwent drastic technical improvements in their design that help to investigate in details the catalytic properties and .. Calorimetry | Chemdemos - University of Oregon. Heat of Neutralization: HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) Heat of Neutralization: The initial temperature of 50.0 mL of 3.0 M HCl and a 3.0 M NaOH are measured using a digital thermometer probe. The HCl and NaOH react a calorimeter. The final temperature of the resultant solution is measured. The heat exchanged between the chemcial reaction and the solution ..